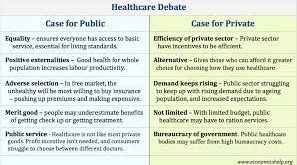
As individuals age, their healthcare needs often become more complex, making health insurance a critical consideration for seniors. With an increasing life expectancy and a growing elderly population, understanding the various health insurance options available for seniors is essential. This article explores the types of health insurance coverage available for older adults, the challenges they face, and the importance of planning for healthcare needs during retirement.
 1. Understanding Health Insurance for Seniors
1. Understanding Health Insurance for Seniors
Medicare: The Foundation of Coverage
- What is Medicare?: Medicare is a federal health insurance program primarily for individuals aged 65 and older. It consists of several parts that cover different aspects of healthcare.
- Part A (Hospital Insurance): Covers inpatient hospital stays, skilled nursing facility care, hospice care, and some home health care.
- Part B (Medical Insurance): Covers outpatient care, preventive services, and some doctor visits.
- Part C (Medicare Advantage): A private insurance plan that combines coverage from both Part A and Part B, often including additional benefits such as vision and dental care.
- Part D (Prescription Drug Coverage): Provides coverage for prescription medications, helping seniors manage their medication costs.
Medicaid: Additional Support
- What is Medicaid?: Medicaid is a state and federal program that provides health coverage for low-income individuals, including seniors who meet certain income and asset criteria. It can help cover costs not fully addressed by Medicare, such as long-term care.
2. Additional Coverage Options for Seniors
Medicare Supplement Plans (Medigap)
- What Are Medigap Plans?: Medigap plans are private insurance policies designed to cover costs that Medicare does not, such as copayments, deductibles, and coinsurance. These plans help reduce out-of-pocket expenses and provide more comprehensive coverage.
Long-Term Care Insurance
- Importance of Long-Term Care: Many seniors may require long-term care services, which are not typically covered by Medicare. Long-term care insurance can help cover the costs of nursing homes, assisted living facilities, or home health care.
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
- Tax-Advantaged Savings: While HSAs are generally used with high-deductible health plans, seniors can benefit from these accounts by using them to save for future healthcare expenses. Contributions are tax-deductible, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free.
3. Challenges Faced by Seniors in Navigating Health Insurance
Complexity of Options
- Understanding Coverage: With multiple options available, seniors may find it challenging to navigate the complexities of health insurance. The varying plans, benefits, and costs can lead to confusion about which options best suit their needs.
Rising Healthcare Costs
- Financial Strain: As healthcare costs continue to rise, many seniors may struggle to afford necessary care, even with insurance coverage. Out-of-pocket expenses can accumulate quickly, especially for those with chronic conditions.
Health Status Changes
- Adapting to New Needs: Seniors often experience changes in health status, which can affect their insurance needs. It’s crucial for them to regularly review and adjust their coverage as their healthcare requirements evolve.
4. The Importance of Planning
Proactive Healthcare Management
- Regular Check-Ups: Seniors should prioritize regular health check-ups and screenings, which can help identify health issues early and reduce long-term costs.
- Understanding Benefits: Familiarizing themselves with the benefits available through their insurance plans can empower seniors to make informed decisions about their healthcare.
Consulting with Experts
- Professional Guidance: Seeking advice from insurance agents, financial planners, or elder care advocates can help seniors navigate their options and choose the best coverage for their needs.
5. Advocacy and Resources
Community Support
- Local Resources: Many community organizations and non-profits offer resources and assistance for seniors in understanding their health insurance options, including Medicare counseling services.
- Government Programs: Programs like the State Health Insurance Assistance Program (SHIP) provide free, unbiased information to help seniors understand their Medicare options and benefits.
 Conclusion
Conclusion
Health insurance is a vital aspect of aging that can significantly impact seniors’ quality of life. By understanding the various coverage options available, recognizing the challenges they face, and proactively planning for their healthcare needs, seniors can navigate the complexities of health insurance more effectively. As the population ages, ensuring that older adults have access to comprehensive and affordable health coverage remains a critical priority for individuals, families, and policymakers alike.